Α D Glucose and Β D Glucose Are
However l-glucose is not a naturally occurring compound in nature and is made in a lab. Eat four pieces of hard candy.
D-glucose and L-glucose are examples of enantiomers.
. The natural form D-glucose is also referred to as dextrose especially in the food industry. Glucose is mainly made by plants and most algae during photosynthesis from water and carbon dioxide using energy from sunlight where it is used to make cellulose in cell walls the most abundant carbohydrate in the world. Wait for 15 minutes and then check your blood sugar again.
In order to determine which of these isomers is actually D-glucose a reference compound of known absolute configuration is needed which can be prepared from or converted to D-glucose. Spot checking from a chemical supplier l-glucose costs over 50 per gram so 400 per teaspoon. According to a study in Human Cell published in July 2015 theres another type of glucose called l-glucose which is a mirror image of d-glucose.
And it is because these 20 amino acids can be found in peptides and proteins of humans and other mammals. E L-glucose cannot form a closed structure. L -Glucose does not occur naturally in living organisms but can be synthesized in the laboratory.
They are non superimposable mirror images of each other. Drink four ounces of regular soda not diet soda. Because the first determination of the absolute.
L-Glucose can rotate plane polarized light in anticlockwise direction. In comparison d-glucose of a similar grade from the same supplier is around 004 per gram so 030 per teaspoon. This is C-5 in glucose.
D-Glucose is a sugar molecule that is abundant in nature. Cagatay M Petrowitsch T Neuser D Petzinna D Rupp M. It is the only sugar unit in cellulose and starch.
As the l -isomer of glucose it is the enantiomer of the more common d -glucose. Some sugars like disaccharides consist of one glucose molecule plus any other monosaccharidel-Glucose is an organic compound with formula C 6 H 12 O 6 or OCHCHOH 5 H specifically one of the aldohexose monosaccharidesAs the l-isomer of glucose it is the enantiomer of the more common d-glucose. In D-glucose three hydroxyl groups and one hydrogen group attach to the right side whereas in L-glucose three hydroxyl groups and one hydrogen group attach to the left side.
As glucose control deteriorates and HbA 1C rises the contribution of fasting plasma glucose becomes more significant. When you see the terms dextrose or glucose theyre referring to the d-glucose form. D-glucose and dextrose are the same.
Glucose is one of the main products of photosynthesis and starts respiration. D only D-glucose is found in disaccharides and polysaccharides. Glucose can be found in the forms of D-glucose.
D and L Notation of Amino Acids. National Center for Biotechnology Information. The D isomer is dextrorotatory and this is indicated by a sign or sometimes confusingly by a lower case d and the L isomer is laevorotatory and this is indicated by a - sign or sometimes by.
National Institutes of Health. Amino acids are also characterized by the D and L notation and just like there is a trend of carbohydrates naturally occurring in D form. Glucose is a simple sugar with the molecular formula C6H12O6.
In groups of patients with HbA 1C of 8 to 9 and 9. A Haworth projection representation of the structure of glucose Glucose C6H12O6 is a hexose -- a monosaccharide containing six carbon atoms. With over a thousand-fold price differential someone along the way would recognize if they were accidentally selling l-glucose.
Glucose is the most abundant monosaccharide a subcategory of carbohydrates. D-glucose is the enantiomer of the L-glucose and we call it dextrose. L-Glucose is a sugar molecule that is less abundant in nature.
Glucose is a simple sugar with the chemical formula C 6 H 12 O 6. In fact the full name for common glucose is D- -glucose and its chemically correct name using theIUPAC systematic naming system for organic molecules is 2R3S4R5R-23456-pentahydroxyhexanol. As enantiomers the two forms have equal and opposite optical rotations.
D- and L-sugars are mirror images of one another. D-Glucose C6H12O6 CID 107526 - structure chemical names physical and chemical properties classification patents literature biological activities safetyhazardstoxicity information supplier lists and more. D and L glucose are enantiomers.
Research is expanding into the field of chiral chemistry quite rapidly because for the most part only. Although many studies on the different aspects of alcoholic fermentation are available in the literature it is still difficult to identify the possible causes of the slowing-down or stuck of fermentations even if the change of some compositional parameters D-glucoseD-fructose and glycerine producedhexoses converted ratios could be assumed as sound signals of a. National Library of Medicine.
D-Glucose is the most common naturally occurring simple sugar and is a building block for disaccharides sucrose and lactose and higher oligo- and polysaccharides. Glucose is mainly manufactured by plants and most of the algae during the process of photosynthesis. There are hundreds of amino acids however we will discuss the stereochemistry of only 20 of them.
Acarbose reduces the risk for myocardial infarction in type 2 diabetic patients. In a Fischer projection the highest numbered chiral carbon has the OH group pointing to the right. B it is not possible to make L-glucose.
L-Glucose does not occur naturally in higher living. Glucose is a widely available monosaccharide and is also known as dextrose and blood sugar. L-Glucose is an organic compound with formula C 6 H 12 O 6 or OCH CH OH 5 H specifically one of the aldohexose monosaccharides.
In a sugar the D or L designation refers to the configuration of the chiral carbon farthest from the aldehyde or keto group. Since D-glucose is an aldohexose it must possess four chiral carbon atoms and can exist in 2 4 16 stereoisomers see Table I. Enantiomers will have the opposite prefixes of each other.
D-Glucose can rotate plane polarized light in the clockwise direction. What is the systematic IUPAC name of glucose. Animals and plants produce D-glucose by.
In simple terms we can say that it is made up of six carbon atoms twelve hydrogen atoms and six oxygen atoms. Drink four ounces of fruit juice. Take four glucose tablets.
Meta-analysis of seven. In energy metabolism glucose is the most important source of energy in all organisms. Do one of the above treatments again until your blood sugar is 70 mgdL or above and eat a snack if your next meal is an hour or more away.
The symbolsD and L specify the stereochemistry of the molecules. Dextrose is the common name used for D-glucose. L-glucose is an organic compound and its IUPAC name is 2S3R4S5S-23456-pentahydroxyhexanal.
One difference between D-glucose and L-glucose is A the open-chain form of L-glucose does not exist. In fact there are 2 forms of glucose the dextrose. The molar mass of glucose and dextrose is the same.
Difference Between Glucose and Dextrose Definition. C L-glucose has a 5-membered ring and D-glucose has a 6-membered ring.

Alpha D Glucose Pentaacetate C16h22o11 Pubchem
D Glucose Monohydrate C6h14o7 Chemspider
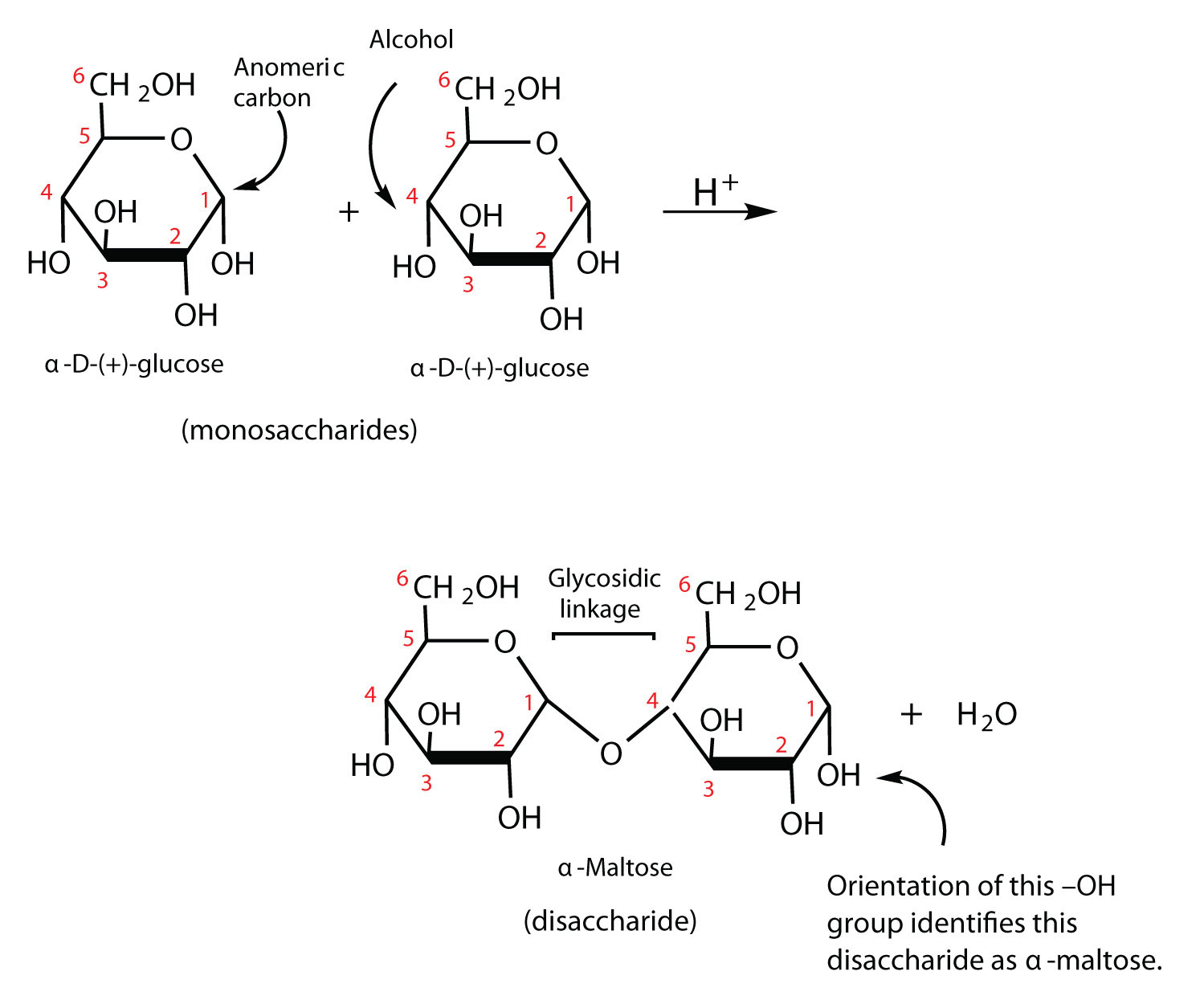
12 6 Disaccharides Chemistry Libretexts

238 Monosaccharide Stock Vector Illustration And Royalty Free Monosaccharide Clipart
No comments for "Α D Glucose and Β D Glucose Are"
Post a Comment